Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Testicular Ultrasound
Test Overview
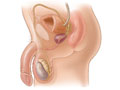
A testicular ultrasound (sonogram) is a test that uses reflected sound waves to show a picture of the testicles and scrotum. The test can show the long, tightly coiled tube that lies behind each testicle and collects sperm (epididymis). And it can show the tube (vas deferens) that connects the testicles to the prostate gland. The ultrasound does not use X-rays or other types of radiation.
A small handheld device called a transducer is passed back and forth over the scrotum. The device sends the sound waves to the computer, which turns them into a picture. This picture is shown on a video screen. The picture produced by ultrasound is called a sonogram, echogram, or scan. Pictures or videos of the ultrasound images may be saved.
Why It Is Done
Testicular ultrasound is done to:
- Check a mass or pain in the testicles.
- Find or check on an infection or swelling of the testicles or epididymis.
- Check for twisting of the spermatic cord. This problem cuts off blood supply to the testicles (testicular torsion).
- Check to see if testicular cancer has come back.
- Find an undescended testicle.
- Check for fluid in the scrotum (hydrocele), fluid in the epididymis (spermatocele), blood in the scrotum (hematocele), or pus in the scrotum (pyocele).
- Guide a biopsy needle for a testicular biopsy. This may be done when testing for infertility.
- Check an injury to the genital area.
How To Prepare
In general, there's nothing you have to do before this test, unless your doctor tells you to.
How It Is Done
A testicular ultrasound is done at a doctor's office or hospital.
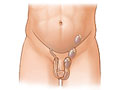
Before the test, you'll need to take off all your clothes from the waist down. You will put on a gown. You'll be asked to lie on your back on a padded table. Folded towels will be used to cover the penis and lift the scrotum. A gel (such as K-Y Jelly) will be spread on your scrotum. This is used for the transducer, which is pressed against your skin and moved across your scrotum many times.
You will need to lie very still during the ultrasound scan. You may be asked to take a breath and hold it for several seconds during the scan.
When the test is finished, the gel is removed from your skin. You may be asked to wait until the radiologist has reviewed the test. He or she may want to do more ultrasound views.
How long the test takes
The test takes about 20 minutes.
How It Feels
Most people don't feel pain during the test. If your scrotum hurts already from an injury or illness, the slight pressure from the transducer may be somewhat painful. You will not hear or feel the sound waves.
Risks
There are no known risks from having this test.
Results
Normal: | The testicles are normal in shape and size. They are in the normal position. |
|---|---|
There is no sign of a noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant) lump in the testicles. | |
There is no sign of infection or swelling of the testicles or epididymitis. | |
There is no twisting of the spermatic cord. This twisting (testicular torsion) cuts off blood supply to the testicles. | |
There is no sign of fluid in the scrotum (hydrocele), blood in the scrotum (hematocele), fluid in the epididymis (spermatocele), or pus in the scrotum (pyocele). | |
Abnormal: | There is a lump in the testicle or there are signs of testicular cancer. |
There are signs of infection or swelling of the testicles or epididymis. | |
The spermatic cord is twisted. This problem cuts off blood supply to the testicles (testicular torsion). | |
No testicle or only one testicle is present in the scrotal sac. | |
Fluid (hydrocele), blood (hematocele), or pus (pyocele) is present in the scrotum or fluid is present in the epididymis (spermatocele). | |
There is a hernia in the scrotum. |
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 31, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.